Uveitis
San Francisco Uveitis Treatment
What is Uveitis?
Uveitis occurs when the middle layer of the eyeball, called the uvea, becomes red and swollen. The inflammation and swelling of the eye may destroy delicate tissues. In addition, uveitis may manifests after an infection, a virus, or an eye injury. As a result, to prevent everlasting problems, seek immediate medical treatment.
Click here to learn about the different types of Uveitis.
Uveitis Services We Offer
As mentioned above, uveitis is a disease that needs to be treated right away. Generally, treatment may include eye drops or other medications. At Pacific Eye Associates, Dr. David Heiden is an excellent and thorough medical doctor who subspecializes in Uveitis and Iritis. Contact us today if your eye is red and/or swollen.
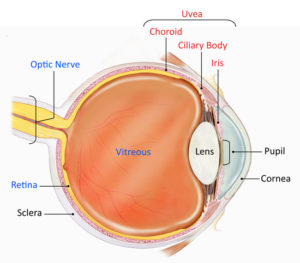
3 Types of Uveitis
There are three different types of uveitis:
- Anterior Uveitis, commonly called Iritis: Is the swelling of the uvea near the front of the eye. Due to the location of the inflammation of the iris and the ciliary body, this variety of uveitis is the most common type of uveitis. Usually, lasting up to 8 weeks.
- Symptoms: Eye redness, eye pain, blurred vision or difficulty seeing normally, light sensitivity (normal light seems too bright)
- Intermediate Uveitis, commonly called IU: Is the swelling of the uvea near the middle of the eye, the cilia body. Once the ciliary body is infected, the disease may last for a few weeks to many years. This type of uveitis may often time be worse before the uvea will get better. IU is the rarest of all three types of uveitis and primarily afflicts children and young adults.
- Symptoms: Same as above; Eye redness, eye pain, blurred vision or difficulty seeing normally, light sensitivity (normal light seems too bright)
- Posterior Uveitis, also known as choroiditis or chorioretinitis: Is the swelling of the uvea towards the back of the eye, involving the retina and choroid. Because the retina and choroid is the source of the infection, choroiditis develops gradually and lasts for many years. Posterior Uveitis is the least common form of uveitis.
- Symptoms: Same as above; Eye redness, eye pain, blurred vision or difficulty seeing normally, light sensitivity (normal light seems too bright)


